Defining Forest and Freshwater Ecosystems
Forest ecosystem freshwater ecosystem drawing easy – Understanding the intricacies of Earth’s diverse ecosystems is crucial for appreciating the delicate balance of life. This section will delve into two vital ecosystems: forests and freshwater systems, exploring their defining characteristics, key components, and highlighting their similarities and differences.Forest ecosystems are complex and dynamic communities dominated by trees. They are characterized by a rich biodiversity, encompassing a vast array of plant and animal life interconnected through intricate food webs.
The key components include trees, which form the structural backbone, along with the understory vegetation, soil, fungi, and a diverse range of animals, from insects to large mammals. The soil plays a critical role, supporting plant growth and acting as a reservoir for nutrients and water. The interaction between these components creates a self-sustaining system.
Forest Ecosystem Characteristics
Forest ecosystems exhibit significant variations depending on climate, geography, and species composition. Tropical rainforests, for instance, are characterized by high rainfall, high biodiversity, and a dense canopy, while boreal forests, found in high-latitude regions, are dominated by coniferous trees adapted to cold climates. Regardless of type, forests provide numerous ecological services, including carbon sequestration, water regulation, and habitat provision.
Eh, drawing forest and freshwater ecosystems is pretty easy, right? Like, you just gotta focus on the basic stuff. But did you know even tiny creatures like earthworms have cool systems? Check out this rad guide on how to draw an earthworm’s respiratory system: earthworm respiratory system easy drawing. It’s a total mind-blower, then get back to your awesome forest and freshwater ecosystem drawings! Easy peasy!
The intricate interplay between sunlight, water, nutrients, and organisms shapes the unique characteristics of each forest type.
Freshwater Ecosystem Characteristics
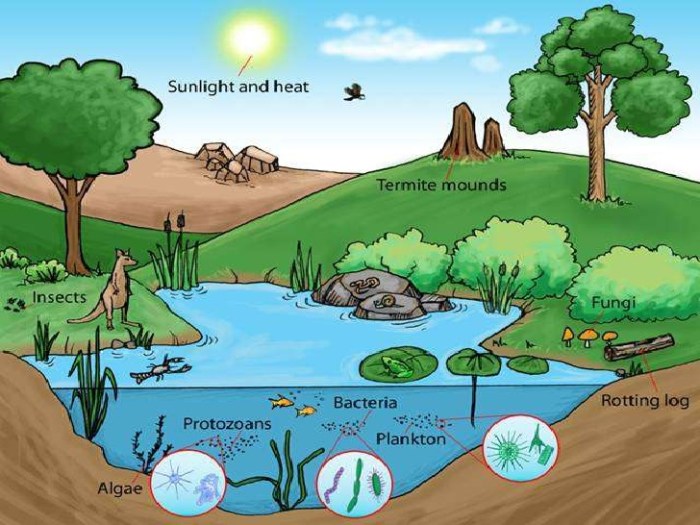
Freshwater ecosystems encompass a wide range of habitats where water is the dominant feature, characterized by low salt concentration. These habitats include lakes, rivers, streams, ponds, wetlands, and springs. Each type possesses unique physical and chemical properties that influence the organisms that inhabit them. Lakes, for example, are characterized by stratified water layers with varying temperatures and oxygen levels, while rivers are characterized by flowing water and constantly changing conditions.
The inhabitants of freshwater ecosystems are incredibly diverse, ranging from microscopic organisms like algae and bacteria to fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals.
Comparing Forest and Freshwater Ecosystems, Forest ecosystem freshwater ecosystem drawing easy
While vastly different in their physical structure and dominant organisms, forest and freshwater ecosystems share some similarities. Both support high biodiversity, complex food webs, and play critical roles in global nutrient cycles. Both are also vulnerable to human impacts such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change. However, their key differences are significant. Forest ecosystems are primarily terrestrial, relying on soil for support and nutrients, while freshwater ecosystems are aquatic, with water as the primary medium.
The dominant organisms differ significantly; trees define the forest, while diverse aquatic life forms dominate freshwater ecosystems. Nutrient cycling and energy flow also operate differently in these two ecosystems. For example, nutrient cycling in forests is heavily influenced by decomposition processes in the soil, while in freshwater systems, it is significantly impacted by water flow and sedimentation.
Easy Drawing Representations: Forest Ecosystem Freshwater Ecosystem Drawing Easy
Creating a visually appealing and informative drawing of a forest ecosystem is a fantastic way to understand its complexity. This section provides a simple guide and design for illustrating a forest ecosystem, perfect for educational purposes or creative expression. Let’s explore how to easily represent this vital biome through drawing.
Simple Forest Ecosystem Drawing
A simplified forest ecosystem drawing can effectively convey the key characteristics of this environment. The following table Artikels a simple design using easily drawn elements. Remember, the goal is clarity and representation, not photorealism.
| Layer | Plants | Animals | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canopy | Tall trees with broad leaves (e.g., oak, maple) | Birds (e.g., owl, woodpecker), squirrels | Draw tall, slightly irregular tree shapes with leafy crowns. Show birds perched on branches and squirrels climbing. |
| Understory | Smaller trees and shrubs (e.g., dogwood, azalea) | Snakes, rabbits | Draw shorter trees and bushy shrubs under the canopy. Add simple snake and rabbit shapes. |
| Forest Floor | Ferns, mushrooms, wildflowers | Insects, deer, foxes | Draw various shapes representing ferns, mushrooms, and simple flowers. Include small insect shapes, a deer, and a fox. |
Step-by-Step Forest Ecosystem Drawing Guide
This guide simplifies the process of drawing a forest ecosystem, making it accessible for children.
- Sketch the Background: Start with a simple line representing the ground. Lightly sketch a horizon line.
- Draw the Trees: Begin with the tallest trees in the background, drawing simple, irregular shapes for the trunks and crowns. Add smaller trees and shrubs in the foreground.
- Add the Understory: Sketch in some smaller bushes and plants beneath the taller trees. Use simple shapes and lines.
- Include the Forest Floor: Add ferns, mushrooms, and flowers to the base of the trees. These can be simple shapes or lines.
- Draw the Animals: Add simple representations of animals like birds, squirrels, rabbits, deer, and insects. Use basic shapes to depict these creatures.
- Add Details: Lightly shade some areas to give the drawing depth and dimension. You can use different shades of green and brown to create variation.
Essential Elements for an Easy Forest Ecosystem Drawing
To effectively communicate the key characteristics of a forest ecosystem, a drawing should include these essential elements:
- Layered Vegetation: Representing the canopy, understory, and forest floor layers is crucial to showing the vertical structure of the forest.
- Variety of Plants: Include different types of trees, shrubs, and ground cover to depict biodiversity.
- Animal Representation: Show a range of animals that inhabit different layers of the forest, highlighting the food web interactions.
- Simplified Detail: Focus on clear representation rather than photorealism. Simple shapes and lines are sufficient.
- Color: Use a range of greens and browns to illustrate the forest’s natural color palette.
Illustrative Examples

Understanding the intricate relationships between forest and freshwater ecosystems requires examining specific interactions. These interactions, often subtle yet powerful, shape the health and productivity of both environments. The following examples illustrate the reciprocal influence these ecosystems exert on each other.
Forest Ecosystem Impact on Freshwater Ecosystem
Imagine a lush forest bordering a clear stream. The forest floor is covered with fallen leaves, branches, and decaying organic matter.
Leaf litter, a significant component of this forest debris, is gradually transported into the stream by rainfall and runoff.
This influx of organic matter provides a vital source of nutrients for aquatic organisms. Bacteria and fungi decompose the leaf litter, releasing essential elements like nitrogen and phosphorus into the water.
These nutrients fuel the growth of algae and other aquatic plants, forming the base of the food web. The increased nutrient levels, however, can also lead to eutrophication in some cases, resulting in algal blooms that deplete oxygen and harm aquatic life. This highlights the complex and sometimes contradictory effects of forest-freshwater interactions.
Freshwater Ecosystem Impact on Forest Ecosystem
Now consider the role of the stream itself on the adjacent forest. The stream acts as a crucial water source for the trees and other plants.
Trees, especially those near the stream bank, draw water from the groundwater system replenished by the stream. This constant water supply supports their growth and overall health, particularly during dry periods. The moisture from the stream also contributes to the humidity levels of the surrounding air, creating a more favorable microclimate for certain plant species.
Conversely, periods of drought or low stream flow can significantly impact the forest, leading to water stress in trees and increased vulnerability to pests and diseases. This demonstrates the direct link between water availability and forest productivity.
Comparative Description of Interactions
Two contrasting interactions exemplify the complex relationship between forest and freshwater ecosystems: nutrient enrichment versus water provision.
The first interaction, the input of leaf litter from the forest into the stream, enriches the aquatic ecosystem with nutrients, fostering increased productivity. However, this enrichment can be detrimental if excessive, leading to eutrophication.
The second interaction, the provision of water from the stream to the forest, supports forest growth and overall health. This is a primarily positive interaction, essential for maintaining forest productivity. However, a reduction in stream flow negatively impacts forest health, demonstrating a crucial dependence of the forest on the freshwater ecosystem.
Key Questions Answered
What are some common misconceptions about forest ecosystems?
A common misconception is that forests are static environments. In reality, forests are dynamic ecosystems constantly changing through processes like succession and disturbance.
How can I make my freshwater ecosystem drawing more realistic?
Add details like varying water depths, aquatic plants, and different types of rocks or substrates to create a more realistic depiction.
What are some simple ways to show the interaction between forest and freshwater ecosystems in a drawing?
Show leaf litter falling into a stream, or depict trees shading a riverbank to illustrate the impact of one on the other.
What are the most important things to include when drawing a forest ecosystem for children?
Focus on the main layers (understory, canopy, forest floor), a few key animals, and simple details to keep it engaging and easy to understand.

